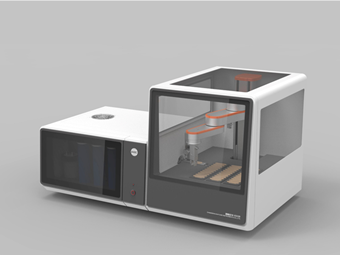
Introduction
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic heavy metal with bioaccumulative properties. It, classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), accumulates in the human body over the long term and causes irreversible damage. Once absorbed, it has a biological half-life of approximately 15 to 30 years. It accumulates primarily in the liver and kidneys, where it can progressively damage multiple organ systems.
Cadmium in durian primarily stems from two sources, environmental contamination and farming practices. Improper discharge of industrial waste leads to cadmium accumulation in soil, and durian trees have a high capacity to absorb and concentrate heavy metals through their roots. Additionally, the inappropriate use of fertilizers is a key factor. In pursuit of higher yields, some growers overapply phosphate fertilizers that contain cadmium (e.g., cadmium-containing diammonium phosphate), which continuously elevates soil cadmium levels, leading to its accumulation in the fruit.
Between 2024 and 2025, 77 batches of durian from Vietnam and 16 batches from Thailand were found to exceed cadmium limits by Chinese customs, with some samples reaching concentrations as high as 0.314 mg/kg, far exceeding the safety limits. As of January 10, 2025, all durian exported to China must be accompanied by a cadmium test report, with a maximum allowable cadmium content of ≤0.05 mg/kg for customs clearance. Each batch requires sampling of 5 samples, with test results to be issued within 72 hours. Rapid, accurate testing methods are therefore essential.
Traditional methods for cadmium determination, such as Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS), are accurate but time-consuming. They involve complex sample pretreatment and require a high level of technical skill, making them unsuitable for rapid, high-throughput cadmium testing in durian samples.
The 5E-AA2288 Automatic Cadmium Analyzer, developed by CKIC, adopts the electrothermal vaporization-atomic absorption method with direct solid sample feeding. It features fast analysis, simple operation, high accuracy, and excellent repeatability. Durian samples require no complex pretreatment and can be analyzed directly, delivering reliable results within 4 minutes.
Principle
The 5E-AA2288 employs the electrothermal vaporization-atomic absorption spectrometry (ETV-AAS). Through high-temperature combustion (pyrolysis), the organic matter in the sample is decomposed, and the volatile substances are further broken down by passing through a catalytic zone, where trace amounts of cadmium are selectively captured by the catalyst. By gently switching the atmosphere, cadmium is released from the ash and the catalyst. It is then introduced into a hydrogen flame for atomization through a uniquely patented interface device. The cadmium content in the sample is directly calculated and obtained through software analysis.
Instruments and Equipment
l 5E-AA2288 Automatic Cadmium Analyzer
l Homogenizer
l Analytical balance with 0.0001g precision
Reagents and Materials
l Certified cadmium standard solution (1000 µg/mL)
l Fresh durian samples
Analysis
l Sample preparation
Remove the shell from the durian and collect about 500 g of pulp from different parts. Homogenize the pulp using a homogenizer and transfer the homogenate into a clean centrifuge tube for testing.
l Instrument preparation
Operate the instrument according to the instruction manual and ensure it is ready for testing.
l Method selection
In the software, click Define Method and then New Method in the dialog box to create a new method; alternatively, select an existing method as needed.
l Test blank sample
l Calibration
A calibration curve is established using the external standard method.
l Sample Analysis
Instrument Parameters:
|
Drying temperature
|
450℃
|
|
Pyrolysis temperature
|
750℃
|
|
Catalysis temperature
|
750℃
|
|
Flow rate
|
280ml/min
|
|
Analysis time
|
80s
|
Analysis Result
A cadmium standard solution with a concentration of 0.145 mg/L was used to prepare the calibration curve. The fitting result is shown below.

Fresh durian pulp samples were tested. Each sample was weighed seven times, with sample masses ranging from 0.2000 to 0.4000 g (accurate to 0.0001 g). The test results are shown in the table below.
|
Sample
|
Sample Mass (g)
|
ZAbs
|
Cadmium Content (ng)
|
Cadmium Concentration (mg/Kg)
|
Mean (mg/kg)
|
SD (mg/kg)
|
RSD (%)
|
|
Durian 1
|
0.3679
|
1.001966
|
6.894618
|
0.019
|
0.018
|
0.00047
|
2.56%
|
|
Durian 2
|
0.3838
|
1.045812
|
7.205575
|
0.019
|
|
Durian 3
|
0.379
|
0.979787
|
6.698571
|
0.018
|
|
Durian 4
|
0.3636
|
0.939826
|
6.415822
|
0.018
|
|
Durian 5
|
0.2015
|
0.544662
|
3.619803
|
0.018
|
|
Durian 6
|
0.2028
|
0.560064
|
3.728787
|
0.018
|
|
Durian 7
|
0.2095
|
0.574888
|
3.833671
|
0.018
|
Conclusion
The test results show an average cadmium content of 0.18 mg/kg, with a relative standard deviation of 2.56%, in the fresh durian pulp samples. This value is well below the regulatory limit of ≤ 0.05 mg/kg for customs clearance, confirming the instrument’s suitability for routine monitoring and compliance testing.


_340x255.png)


_340x255.png)